Difference between revisions of "Dot"
From Linuxintro
imported>ThorstenStaerk |
imported>ThorstenStaerk (→Layout) |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
= Layout = | = Layout = | ||
You can use several layouts: dot, twopi, neato and circo. Here is the neato layout: | You can use several layouts: dot, twopi, neato and circo. Here is the neato layout: | ||
| + | |||
[[File:Layout-neato.png]] | [[File:Layout-neato.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sourcecode for the above: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | digraph "Wikimap" { | ||
| + | layout=neato | ||
| + | overlap=false | ||
| + | "OS" -> "OpenSource" | ||
| + | "OpenSource" -> "Linux" | ||
| + | "OpenSource" -> "BSD" | ||
| + | "BSD" -> "NetBSD" | ||
| + | "BSD" -> "FreeBSD" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
= See also = | = See also = | ||
Revision as of 13:12, 29 May 2016
Dot is a program from the graphviz package to draw graphs from the command line. It can, among other usages, be used to create MindMaps.
Contents
Mindmap
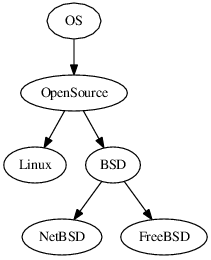
Here's how you create a mindmap with dot:
source.txt
digraph "Wikimap" {
"OS" -> "OpenSource"
"OpenSource" -> "Linux"
"OpenSource" -> "BSD"
"BSD" -> "NetBSD"
"BSD" -> "FreeBSD"
}
create the graphical map
$ dot -Tps -o mindmap.ps source.txt
view the graphical map
$ konqueror mindmap.ps
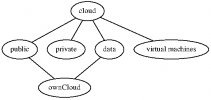
remove arrows
Here is how you draw a mindmap without arrows, you use "arrowhead=none":
source.txt
digraph "Wikimap" {
"cloud" -> "public" [arrowhead=none]
"cloud" -> "private" [arrowhead=none]
"cloud" -> "data" [arrowhead=none]
"cloud" -> "virtual machines" [arrowhead=none]
"data" -> "ownCloud" [arrowhead=none]
"public" -> "ownCloud" [arrowhead=none]
}
create the graphical map
$ dot -Tps -o mindmap.ps source.txt
view the graphical map
$ konqueror mindmap.ps
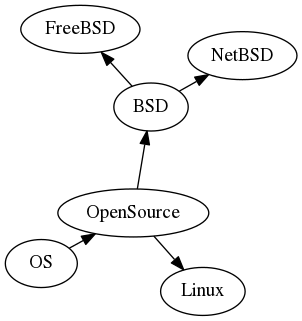
Layout
You can use several layouts: dot, twopi, neato and circo. Here is the neato layout:
Sourcecode for the above:
digraph "Wikimap" {
layout=neato
overlap=false
"OS" -> "OpenSource"
"OpenSource" -> "Linux"
"OpenSource" -> "BSD"
"BSD" -> "NetBSD"
"BSD" -> "FreeBSD"
}